AI in Qatar Blue Collar Recruitment: The transformation sweeping through Qatar’s recruitment landscape is nothing short of revolutionary. At MahadManpower.com, we’re pioneering how AI in Qatar blue-collar recruitment reshapes the entire hiring ecosystem for construction workers, technicians, operators, and skilled labourers. This isn’t just an upgrade it’s a complete reimagining of how Qatar builds its workforce for ambitious mega-projects and sustained economic growth.
AI in Qatar blue collar recruitment addresses critical pain points that have plagued the industry for decades. From lengthy processing times to compliance complexities, artificial intelligence provides solutions that seemed impossible just years ago. As Qatar accelerates its National Vision 2030 and continues massive infrastructure development, the need for efficient, accurate, and scalable recruitment has never been more urgent. Required skills example key job.
AI in Qatar Blue Collar Recruitment: Fast-Track Success
Revolutionizing Speed Without Sacrificing Quality
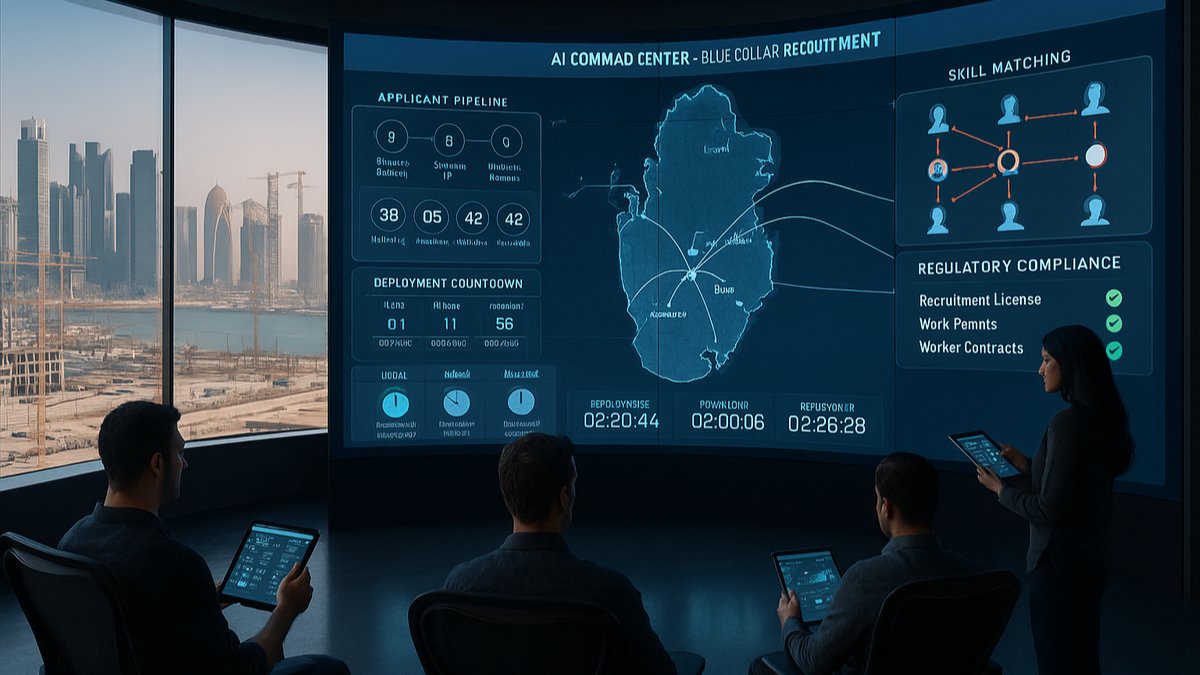
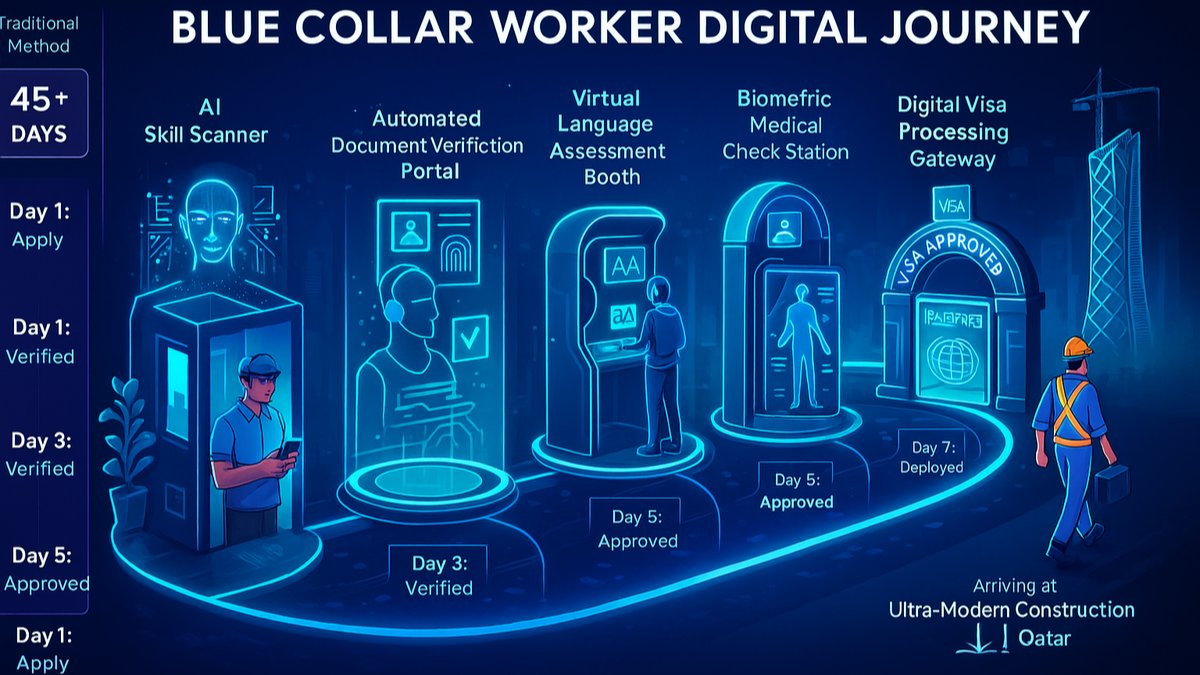
Traditional blue-collar recruitment in Qatar typically takes 30-60 days from initial application to deployment. AI in Qatar blue collar recruitment slashes this to just 5-10 days while actually improving candidate quality. How? AI simultaneously processes multiple verification layers that would traditionally happen sequentially. Key job roles required skills.
While human recruiters handle one application at a time, AI systems process thousands simultaneously. They verify documents, validate skills, check medical fitness, confirm visa eligibility, and match candidates to specific job requirements all within minutes. This parallel processing revolutionises recruitment timelines without cutting corners on essential checks.
Intelligent Skills Matching Beyond Keywords
The sophistication of AI in Qatar blue collar recruitment extends far beyond simple keyword matching. Advanced algorithms understand the nuances of blue-collar skills, recognising that a “crane operator” in the Philippines might have different certifications than one from India, but both could be equally qualified for Qatar projects. Skills example key job roles.
AI analyses work history patterns, project types, and even climate conditions of previous deployments. A worker who thrived on offshore platforms might excel at Qatar’s coastal projects. Someone with desert construction experience adapts faster to Qatar’s environment. These insights create matches that human recruiters might miss, leading to better placement success rates.
Automated Compliance and Documentation
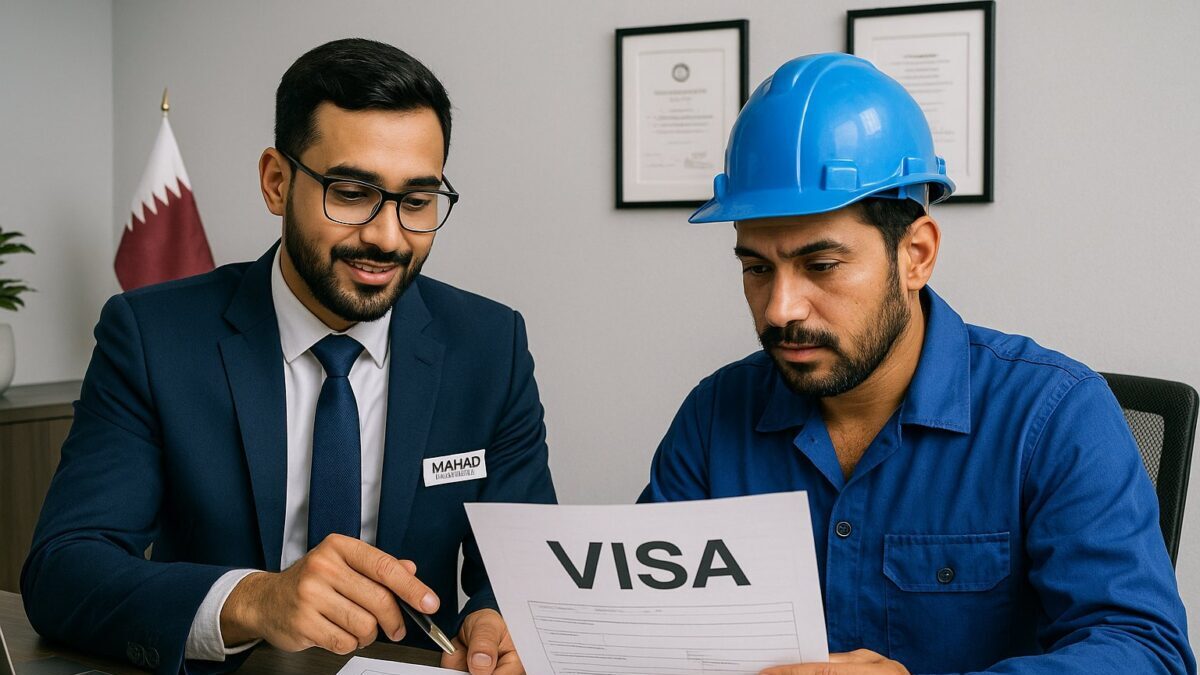
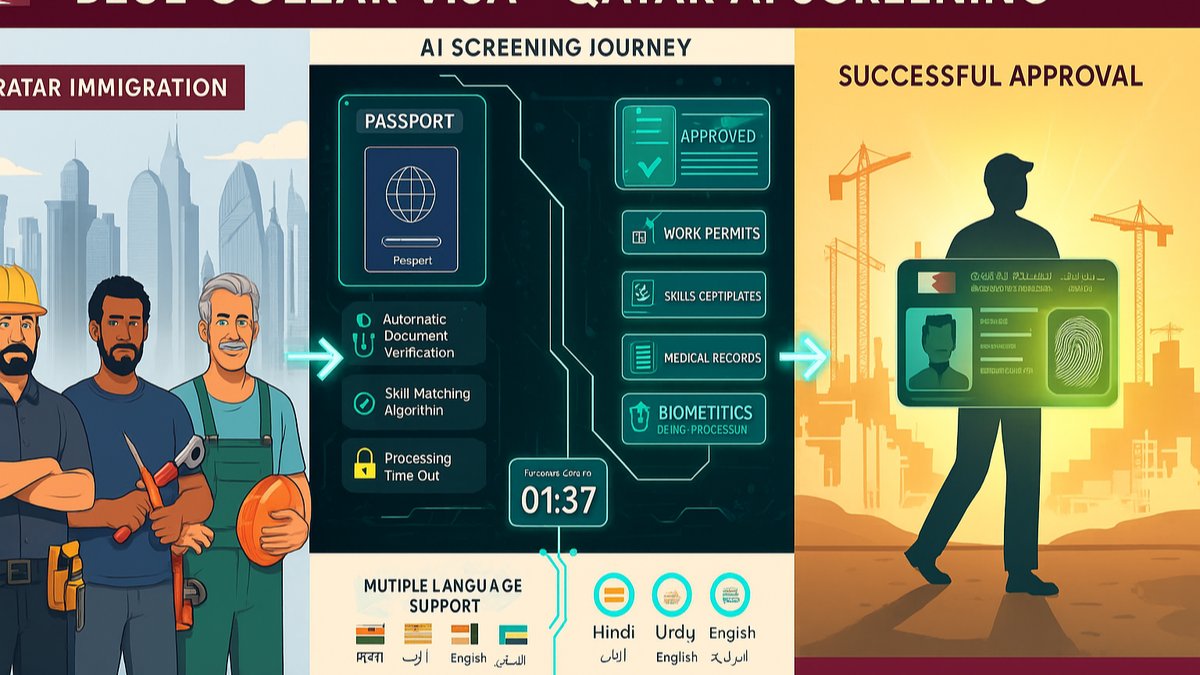
Qatar’s regulatory framework for blue-collar workers involves complex documentation requirements. AI in Qatar blue collar recruitment transforms this challenging aspect through intelligent automation. The system tracks changing regulations, ensures all documents meet current standards, and flags potential issues before they cause delays.
Consider the typical documentation needs: passport validity, NOC requirements, attestation status, medical certificates, police clearances, and trade licences. AI manages these simultaneously, sending automated reminders for renewals and immediately identifying when documents need updating. This proactive approach prevents last-minute surprises that derail deployments.
Language Assessment and Safety Readiness
Safety is paramount in Qatar’s construction and industrial sectors. AI in Qatar blue collar recruitment includes sophisticated language assessment specifically focused on safety communication. Rather than generic language tests, AI evaluates whether workers can understand emergency instructions, read safety signs, and communicate hazards effectively.
The technology adapts assessments based on job roles. A crane operator needs different communication skills than a general labourer. By tailoring evaluations to specific positions, AI ensures workers can maintain safety standards from day one, reducing accidents and improving project outcomes.
Predictive Analytics for Long-term Success
One groundbreaking aspect of AI in Qatar blue collar recruitment involves predictive analytics for worker retention and performance. By analysing patterns from thousands of successful placements, AI identifies factors that correlate with long-term success in Qatar’s work environment. Blue collar workers.
These predictions consider multiple variables: previous contract completion rates, adaptation to similar climates, experience with multinational teams, and even family status. Workers identified as high-retention candidates receive priority processing, reducing costly turnover that disrupts projects and increases recruitment expenses.
Cost Efficiency and ROI Impact
The financial benefits of AI in Qatar blue collar recruitment extend throughout the entire employment lifecycle. Faster recruitment means projects start sooner. Better matching reduces early termination costs. Automated compliance prevents expensive legal issues. Combined, these efficiencies deliver remarkable ROI.
Our clients report average cost reductions of 45% per hire when using AI-powered recruitment. For large projects requiring hundreds or thousands of workers, these savings translate to millions of riyals. More importantly, improved worker satisfaction and retention create stable, productive workforces that deliver projects on time and within budget.
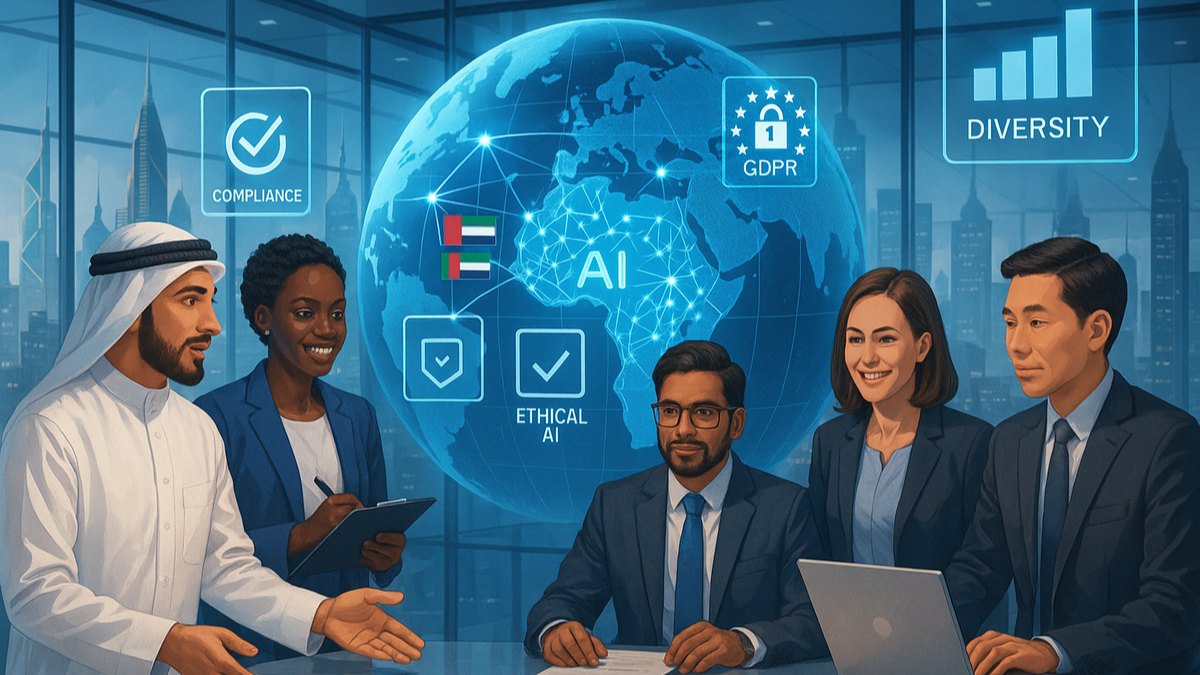
Ethical AI and Worker Protection
Responsible implementation of AI in Qatar blue collar recruitment prioritises worker welfare alongside efficiency. Our AI systems flag potentially exploitative job postings, ensure wage offerings meet legal minimums, and identify recruiters with poor track records. This protective layer shields vulnerable workers while supporting ethical employers.
AI also promotes transparency by providing workers with clear information about job conditions, accommodation standards, and actual take-home pay after deductions. This transparency builds trust and reduces disputes, creating better outcomes for all stakeholders.
Partner with Innovation
The future of AI in Qatar blue collar recruitment holds even greater promise. Emerging technologies like blockchain verification, biometric authentication, and advanced predictive modelling will further streamline processes while enhancing security and reliability.
Don’t let outdated recruitment methods slow your projects. MahadManpower.com combines cutting-edge AI technology with deep market expertise to deliver the blue-collar workforce Qatar’s ambitious projects demand. Contact us today to transform your recruitment process and gain the competitive edge that only AI can provide.